Understanding grease technical data
This is
an excerpt of the main terms mentioned in grease technical data with reference to ASTM tests and further tests on bearings and Gears based on test rigs and manufacturer's requirements.These are required to study and compare various greases - data given in data sheets.
Though there are some maker specific tests for Bearings and other applications, this is a comprehensive general list of tests carried out .
Though there are some maker specific tests for Bearings and other applications, this is a comprehensive general list of tests carried out .
Consistency
ASTM D 217 - Cone
Penetration of Lubricating Grease Depth,
in tenths of a millimeter, a 150-g (0.33-lb) cone penetrates the surface of
worked Grease and unworked grease at 25 °C (77 °F) in 5 seconds.
ASTM D 1403 - Cone
Penetration of Lubricating Using One-Quarter and One-Half Scale Cone is used
when only a small amount of
grease is available.
A measure of the stiffness of a grease. A proper consistency
will make the grease stay in the bearing without generating too much friction.
It is classified according to a scale developed by the NLGI (National
Lubricating Grease Institute). The softer the grease, the lower the number. The test measures how deep a
cone falls into a grease sample in tenths of mm.
Classification of greases by NLGI
consistency number
|
||
NLGI
number |
ASTM worked
penetration (10–1 mm) |
Appearance
at room temperature |
000
|
445–475
|
very fluid
|
00
|
400–430
|
fluid
|
0
|
355–385
|
semi-fluid
|
1
|
310–340
|
very soft
|
2
|
265–295
|
soft
|
3
|
220–250
|
medium hard
|
4
|
175–205
|
hard
|
5
|
130–160
|
very hard
|
6
|
85–115
|
extremely hard
|
Sliding friction test is done to evaluate the grease condition between surfaces subjected to high loads and vibration-This is a measure of groove forming tendency and sliding friction coefficient is evaluated based on the groove.
Temperature
range and Oxidation stability
ASTM D 3232 - Measurement of Consistency of Lubricating Greases at High Temperatures: Can also indicate flow at high temperatures. Grease in a cylindrical opening in an aluminum block is heated at a rate of 5 °C (10 °F)/min while a trident probe turns at 20 rpm in the grease. A Brookfield viscometer attached to the probe measures torque at temperature increments. From this, apparent viscosities are determined at different temperatures
ASTM D 3232 - Measurement of Consistency of Lubricating Greases at High Temperatures: Can also indicate flow at high temperatures. Grease in a cylindrical opening in an aluminum block is heated at a rate of 5 °C (10 °F)/min while a trident probe turns at 20 rpm in the grease. A Brookfield viscometer attached to the probe measures torque at temperature increments. From this, apparent viscosities are determined at different temperatures
ASTM D 942 - Oxidation Stability of Lubricating
Greases by the Oxygen Bomb Method
Indicates oxidation from storage when grease charged with
oxygen at 758 kPa (110 psi) is sealed in a “bomb” at 99°C (210 °F). As grease
oxidizes, it absorbs oxygen. Pressure is recorded at time intervals and degree
of oxidation is determined by the corresponding drop in oxygen pressure.
ASTM D 3336 - Performance Characteristics of in
Lubricating Greases in Ball-Bearings at Elevated temperatures :There are no ASTM tests for
oxidation service, but this test relates oxidation stability to failure rate of
bearings at desired elevated temperatures.
ASTMD 972 - Evaporation and Oils Loss of Lubricating
Greases / D 2595- Evaporation Loss
of Lubricating Greases over Wide-Temperature Range: Two liters per minute of heated air is passed
over grease inside a chamber for 22 hours. Temperature range is 100 - 150 °C
(212 - 302°F) for D 972 and 93 - 315 °C (200 - 599 °F) for D 2595. Evaporation
is calculated from grease weight loss, in percent.
ASTMD 1478 - Determination of resistance of roller bearing greases at low temperature- Bearing is tested at -54 °C for 1.5 Hrs at 454 gms radial load inclusive of tilt.Force to overcome friction and temperature is measured- converted to Friction torque.
Comprehends the suitable working
range of the grease. It goes between the low temperature limit (LTL) and the
high temperature performance limit (HTPL). LTL is defined as the lowest
temperature at which the grease will allow the bearing to be started up without
difficulty. Below this limit, starvation will occur and cause a failure.
Above HTPL, the grease will degrade in an uncontrolled way so that grease life
cannot be determined accurately.
Upper service life (DIN 51 821)is evaluated by running the bearing under a load of 1500,3000 , 4500N - speeds of 3000 ,6000 rpm and temperature varying between 120 to 200
Upper service life (DIN 51 821)is evaluated by running the bearing under a load of 1500,3000 , 4500N - speeds of 3000 ,6000 rpm and temperature varying between 120 to 200
°C- subjecting the bearings to medium speeds and medium axial loads and evaluated as per Weibull distribution curve
Dropping
point
ASTM D 566 -Dripping point
of lubricant grease / D 2265 -
Dropping Point of Lubricating Grease over Wide-Temperature Range - Grease
and a thermometer are placed in a cup inside a test tube and heated until a
drop falls through the cup That temperature is the dropping point. The test
tube assembly is heated in an oil bath for D 566 and inside an aluminum block
oven for D 2265..
Temperature at which a grease
sample, when heated, will begin to flow through an opening according to DIN ISO
2176. It is important to understand that this point is considered to have
limited significance for performance of the grease as it is always far above
HTPL.
Viscosity
Apparent viscosity /
pumpability :
ASTM D 1092 -
Measuring Apparent Viscosity of Apparent viscosities at 16 shear rates are
Lubricating Greases :Determined by
measuring the hydraulic pressure on a floating piston which forces grease
through a capillary tube. Eight different capillary tubes and a 2-speed
hydraulic gear pump are used.
A measure of a fluid’s resistance to
flow. For lubricants, a proper viscosity must guarantee an adequate separation
between surfaces without causing too much friction. According to ISO standards,
it is measured at 40 °C (105 °F), as viscosity changes with temperature. Values
at 100 °C (210 °F) allow calculation of the viscosity index, e.g. how much the
viscosity will decrease when temperature rises.
Mechanical
stability
ASTM D 1831- Roll
Stability of Lubricating Grease A 5- kg (11-lb) roller and 50 g (0.11 lb) of
grease are put into a 165-rpm
revolving chamber for 2 hours at room temperature. The difference in penetrations
measured before and after rolling is an indicator of shear stability.
A wear below 7 mg indicates good fretting protection.
ASTM D 1263 - Leakage Tendencies of Automotive Wheel Bearing Greases :A seal-less, grease-packed wheel bearing encircled by a collector ring is spun for 6 hours at 660 rpm at 105 °C (221 °F). Grease thrown off into the ring is weighed and leakage is determined
ASTM D 1263 - Leakage Tendencies of Automotive Wheel Bearing Greases :A seal-less, grease-packed wheel bearing encircled by a collector ring is spun for 6 hours at 660 rpm at 105 °C (221 °F). Grease thrown off into the ring is weighed and leakage is determined
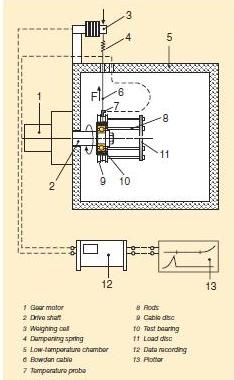
V2F grease test rig
The consistency of bearing greases
should not significantly change during its working life. Three main tests are
normally used to analyse this behaviour:
- Prolonged penetration
The grease sample is subjected to 100 000 strokes in a device called a grease worker. Then, the penetration is measured. The difference against penetration at 60 strokes is reported as the change in 10–1 mm.
- Roll stability
A grease sample is placed in a cylinder with a roller inside. The cylinder is then rotated for 72 or 100 hours at 80 or 100 °C (175 or 210 °F) (the standard test demands just 2 hours at room temperature). At the end of the test period, once the cylinder has cooled to room temperature, the penetration of the grease is measured and the change in consistency is reported in 10–1 mm.
- V2F test
A railway axlebox is subjected to vibration shocks of 1 Hz from a bouncing hammer producing an acceleration level between 12–15 g. After 72 hours at 500 r/min., the grease leaked from the housing through the labyrinth seal is collected in a tray. If it weighs less than 50 g, a rating of ‘m’ is granted, otherwise it is rated as ‘fail’. Afterwards, the test is continued for another 72 hours at 1 000 r/min. If less than 150 grams of grease leaked after completion of both tests, then a rating of ‘M’ is given.
Corrosion and rust
Resistance
ASTM D 1743 -A
grease-packed bearing is spun for 1-minute at 1750 rpm. Excess grease is thrown
off and a thin layer remains on bearing surfaces. The bearing is exposed to
water and stored for 48 hours at 52 °C (125 °F) and 100% humidity. It is then
cleaned and examined for corrosion.
ASTM D 4048 - Detection of Copper Corrosion from Lubricating Grease
A copper strip is immersed in grease inside a covered jar
and heated in an oven or liquid bath for a specified time. The strip is
removed, washed, and compared and classified using the ASTM Copper Strip
Corrosion Standards.
The result is rated by a numerical system and a rating above 2 indicates
poor protection.This test is to assess Lubricating greases should protect copper alloys used in bearings from corrosive attack while in service.
Emcor grease test rig
Corrosive environments demand
special properties for rolling bearing greases. During the Emcor test, bearings
are lubricated with a mixture of grease and distilled water. At the end of the
test, a value between 0 (no corrosion) and 5 (very severe corrosion) is given.
Salt water, instead of distilled water or continuous water flow (washout test),
can be used to make the test more severe.
Water
resistance
Rated 1 to 3 (Loss of Weight , l <10% , 10%<2<30% , 3 >30%)
ASTM D 1264 - Determining the Water Washout
Characteristics of Lubricating Greases:Measures grease washout of a bearing
turning at 600 rpm with water flowing at 5 mL/sec for 1hour at 38 °C (100 °F)
and 79 °C (175 °F).
ASTM D 4049 - Determining the Resistance of Lubricating
Grease to Water Spray :Measures removal of grease 0.8 mm (1/32 in) thick on a plate by water
through a nozzle for5 minutes at 38 °C (100 °F) and 275 kPa (40psi).
Extreme
pressure (EP) performance
ASTM D 2266 - Wear Preventive
Characteristics of Lubricating
Grease (Four-Ball Method) :A rotating steel ball is pressed against three
grease-coated, stationary steel balls for 60 minutes. Scar diameters on the
three stationary balls are relative measures of wear. Balls are 12.7 mm (0.5 inch). Applied load is 40
kgf (392N) rotating at 1200 rpm. Temperature is 75 °C(167 °F).
ASTM D 2596 -
Measurement of Extreme-Pressure Properties of Lubricating Grease (Four-Ball
Method) Same steel ball setup
as above, but load is incrementally increased every 10 seconds until seizure
occurs. This is the weld point. Load wear index is then calculated.
Maximum load is 800 kgf (7845 N) rotating
at 1770 rpm Temperature is 27 °C (80 °F).
ASTM D 2509 - Measurement of Extreme Pressure Properties
of Lubricating Grease (Timken Method) :The outer edge of a continuously
grease-fed bearing race rotates at 800 rpm and rubs against a fixed steel block
for 10 minutes. Successive runs are made with increasingly higher loads and any
surface scoring is reported. Grease is applied at 25 °C (77 °F).The Timken OK
load is the highest load in which no scoring occurs.
The 4-ball weld load test rig uses
three steel balls held in a cup. A fourth ball is rotated against the three
balls at a given speed. A starting load is applied and increased at
pre-determined intervals until the rotating ball seizes and welds to the
stationary balls. Values above 2 600 N are typically expected in EP grease.
Under the 4-ball wear scar test, SKF applies 1 400 N (standard test uses 400 N)
on the fourth ball during 1 minute. The wear on the three balls is
measured and values below 2 mm are considered as appropriate values for EP
greases.
False brinelling test : This is a bearing specific test carried out by subjecting the bearing to a slight oscillation , rolling and sliding movements, under a constant load (5000N load , 5 or 50Hrs , 24Hz , +/- 3 Degrees , temp range +/- 25 °C)- The wear in metal (mg) and grooving is expressed .
FZG Gear test- Flender(Four square gear oil testerDIN 51354, A/2.76/50 Fail Stage) : This is used to evaluate the wear rate of Gear trains subjected to a surface speed of 8.3 m/sec, subjected to lubrication at a load of 1547 N/mm2 , for 100 Hrs (short test) and 300 hrs (long test)- wear or pitting is expressed in mg/kWh.
Oil
separation
Oil separation test :
Vogel / Marawe Test : This is done by heating the specimen to a constant temperature and a filter paper is place below the compression plate. The cylinder movement is measured for 3 seconds and later 24 hrs. The thickness of hardened grease is estimated as the pressure hardening tendency of grease.
Vogel / Marawe Test : This is done by heating the specimen to a constant temperature and a filter paper is place below the compression plate. The cylinder movement is measured for 3 seconds and later 24 hrs. The thickness of hardened grease is estimated as the pressure hardening tendency of grease.
Lubrication
ability
R2F grease test rig
The R2F test assesses the high
temperature performance and lubricating ability of a grease. A shaft with two
spherical roller bearings in their respective housings is driven by an electric
motor. The bearings are run under load, the speed may be varied and heat can be
applied. The test method is carried out under two different conditions after
which the wear of the rollers and the cage is measured. Test A is conducted at
ambient temperature and a “pass” rating means that the grease can be used to
lubricate large bearings at normal operating temperatures and also in low
vibrating applications. Test B runs at 120 °C (250 °F) and a “pass” rating
indicates suitability for large bearings at high temperatures.
Rolling
bearing grease life
R0F+ grease test rig
The R0F and ROF+ tests determine the
grease life and its high temperature performance limit (HTPL). Ten deep groove
ball bearings are fitted into five housings and filled with a given quantity of
grease. The test is undertaken at a pre-determined speed and temperature.
Axial and radial loads are applied and the bearings run to failure. The time to
failure is recorded in hours and a Weibull life calculation is made to
establish the grease life. This information can then be used to determine
re-lubrication intervals in an application.
SKF - be quiet Gear noise test with a scale of GN4 to GN x- GN4 being the best performance.
Bearing noise and vibration testers - are as per bearing maker quality standards.
|
|
|||||||










Informative and interesting Blog! Beautifully written, as usual, I like the post. Thank you so much for nice sharing with us. Keep posting!
ReplyDeleteBest Grease for High Speed Bearings
Nice post! thanks for sharing with us. if you are looking for best grease or industrial lubricant then you can visit DM-Schmierstoffservice GmbH.
ReplyDeleteDM Schmierstoffe is providing all branded premium quality grease with fast shipping and worldwide delivery service. For any lubricant products, you should check it out here: https://schmierstoffe-dm.de/
DeleteHi! this is good information about
ReplyDeletegrease manufacturers in india.. We are also known as a good grease manufacturers. We have a good collection of many types of bearing grease equipments.
Get high-temperature wheel bearing grease, certified by the National Lubricating Grease Institute (NLGI) for automotive wheel bearings at Petron Plus Direct. Visit us now!
ReplyDelete"Understanding grease technical data is crucial for optimal performance. Key factors like the Shear Stability Index ensure durability under stress."
ReplyDelete